In this guide, you’ll learn how to use Port Knocking Daemon knockd to secure SSH Connection and Hardening you server.
Scenario and Abstraction
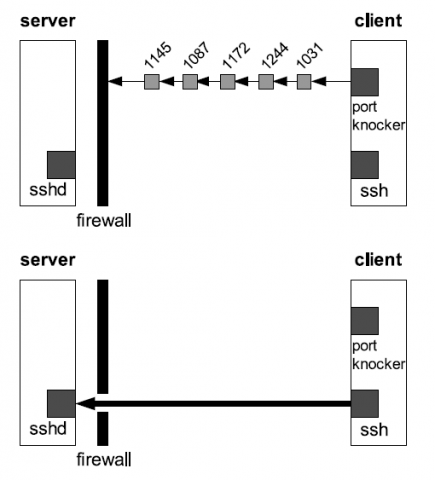
Port knocking as an Idea and Technique, is a method to externally open ports that, by default, the firewall keeps closed.
It works by issues requiring connection attempts to (
a series of predefined closed ports,
&& in a specific sequence and specific connection protocol (ie TCP/UDP). )
When the correct sequence of port “knocks” connection attempts is received by server side,
the server firewall will opens certain port(s) (we’ll focus here on ssh service.) to allow a connection.
This Port Knocking technique can be implemented using only IPtables in advanced way,or using Port-Knocking daemon knockd which we will learn here in this article.
Note
- This guide, runs on Updated CentOS 7 that build with
Latest 64 bitkernel.- Running FirewallD, you can review Introduction to FirewallD on CentOS linode tutorial here.
We’ll Firewall-ed and deny all public SSH connection service at Server-Side,
but just gives SSH pass and and open the gate to allow connection,
only for knocker IP address who do correct knocking (sending packets) for a predefined and specific sets of closed ports (in correct sequence and correct connection protocol) .
so for right knocker the knockd service will fire a open gate firewall-cmd rule for its IP address ,
also can fire closed gate rule for it.
Note
default settings for
firewalldis to allowingsshservice for public-zone, so you may need to make sure to removesshform allowed service.Remove ssh access service permanent from firewall public-zone “assumed as our work default zone”.
firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-service=ssh --permanent firewall-cmd --reload
Steps Server side
Installation
for install Port Knocking on CentOS 7, I would recommend using rpm package of knock-server from nux-dextop repository. but suing direct link for rpm package just as below
rpm -ivh http://li.nux.ro/download/nux/dextop/el7Server/x86_64/knock-server-0.7-1.el7.nux.x86_64.rpm
Note
for more information about
nux-dextopand centos repositories, you can review Available Repositories for CentOS.
if you need to installnux-dextoprepository, and because its coexist with Fedora EPEL, you must install both repos and for EL7 use:
yum -y install epel-release && rpm -Uvh http://li.nux.ro/download/nux/dextop/el7/x86_64/nux-dextop-release-0-5.el7.nux.noarch.rpm
Configuring Knock-server
the configuration file has the name knockd.conf and is located at etc directory /etc/knockd.conf.
our configuration will be settings like below file.
file:/etc/knockd.conf
[options] UseSyslog logfile = /var/log/knockd.log [OpenSSH] Sequence = 3333,4444,5555 Seq_timeout = 15 Tcpflags = syn Command = /bin/firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-rich-rule="rule family="ipv4" source address="%IP%" service name="ssh" accept" [CloseSSH] Sequence = 6666,7777,8888 Seq_timeout = 15 Tcpflags = syn Command = /bin/firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-rich-rule="rule family="ipv4" source address="%IP%" service name="ssh" accept"
in the above configuration settings for knockd we used two knocks. The first will allow the knocker to connect sshd, and the second will close the connection, when the knocker is complete.
- The option
UseSyslog: mean that, theknockdwill logging message usingrsyslogdinserting into /var/log/knockd.log file. Seq_Timeoutis the time in seconds that to wait for a sequence to complete, or will ignore received knocks and start over.tcpflagsOnly pay attention to packets that have this flag set.SequenceSpecify the sequence of ports in the special knock. Optionally, you can define the protocol to be used on a per-port basis (but default is TCP) iesequence = 2222:udp,3333:tcp,4444:udp.start_commandSpecify the command to be executed when a client makes the correct port-knock. All instances of %IP% will be replaced with the knocker’s IP address.commandSpecify the command to be executed when when a client makes the correct port-knock to close the connection.
Note
IN EL7/CentOS 7, FirewallD is a frontend controller and wrapper for iptables, you can review the very nice article Introduction to FirewallD on CentOS at
caution
Above configuration settings are for testing of
knockd.config, you must change at least the ports numbers and sequence and customize it for your server.
while testing will be good to run Lish for emergency.
Run Knockd as Daemon
because of knockd is not a native service you can use to start knockd at boot
chkconfig knockd on
start the knockd service
service knockd start
Note
you may get error message like
Starting knockd: could not open eth0: eth0: No such device exist
so you can adjustment the Ethernet device interface card name from the config file/etc/sysconfig/knockd
Change eth interface device if needed /etc/sysconfig/knockd.
file:/etc/sysconfig/knockd
OPTIONS="-i eth0"
Using from Client side
Installation
Installing Port Knocking knokd client package as:
rpm -ivh http://li.nux.ro/download/nux/dextop/el7Server/x86_64/knock-0.7-1.el7.nux.x86_64.rpm
Run Knockd and Make send a sequence
Now we have to use of knock command from our client we issue the command:
knock -v 3333 4444 5555
- You can examine the logs by accessing the server where knockd-server is located to see the logs about the processes we are doing. you can see logs like followings and notice that, Stage 1, 2 and 3 are passed and the necessary command is executed. So the server is ready for ssh access.
Firing knocks form Client Device (local IP: ‘192.168.1.10’) to Server (local IP: ‘192.168.1.103’):
[root@server ~]# knock -v 192.168.1.103 3333 4444 5555 hitting tcp 192.168.1.103:3333 hitting tcp 192.168.1.103:4444 hitting tcp 192.168.1.103:5555
and Server side log will be as following
[2017-01-01 01:33] starting up, listening on eno16777736 [2017-01-01 01:33] 192.168.1.10: OpenSSH: Stage 1 [2017-01-01 01:33] 192.168.1.10: OpenSSH: Stage 2 [2017-01-01 01:33] 192.168.1.10: OpenSSH: Stage 3 [2017-01-01 01:33] 192.168.1.10: OpenSSH: OPEN SESAME [2017-01-01 01:33] OpenSSH: running command: /bin/firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-rich-rule="rule family="ipv4" source address="192.168.1.10" service name="ssh" accept"
and for check firewall rules changes to allow my client IP.
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --list-all public (active) target: default icmp-block-inversion: no interfaces: eth0 sources: services: ports: protocols: masquerade: no forward-ports: sourceports: icmp-blocks: rich rules: rule family="ipv4" source address="192.168.1.10" service name="ssh" accept
and so:
- To open the port on the server side
knock -v 3333 4444 5555 - To access your server side ssh
ssh [user]@ -p [SSHPortNumber] - To close the connections mean that, to remove the IPtable rule that related to your IP address.
knock -v 6666 7777 8888
Note
from any client you can use same knock-client technique to open or close gates for you, for our scenario here, all we need is to send 3 tcp packet to a specific Ports targets server IP address.
That can be doing using many network application ie nmap, windows knockknock, netcat,telnet, or others.
for using nmap to knock server and open/close gate you can use the below comman suitable with our scenario/example.
but I think you many need to extend theSeq_timeoutvalue
nmap -Pn -p 6666 192.168.1.103 >/dev/null && nmap -Pn -p 7777 192.168.1.103 >/dev/null && nmap -Pn -p 8888 19 2.168.1.103 >/dev/null
from nmap command, now you send 3 tcp packets (knocks) to the server targets the specific predefined port sequence
and now you get the gate closed after you,and also may use nmap to open it and makes a ssh connection again.
Others Port knocking
Port Knocking as technique and policy to open gate for correct knocker who are knocking in predefined sequence, can be presented suing IPtables
Next Steps
First, remember to be sure that you have followed linode guide to Securing Your Server.
Second, you may need to apply two-factor authentication for more secure SSH connection and hardening your server, you can review this linode Ubunto|debian guide about how to Use Google Authenticator to enable two-factor authentication for SSH connections..