In this lab we’ll try to install Odoo 15 the OpenERP on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS, Odoo is a Python-based ERP application, so we will go to use Virtualenv, and we will
- Update Ubuntu
- Install Python, PIP
- Install PostgreSQL Database
- Install And Configure Odoo 15
- Use Nginx As A Reverse Proxy
Step1: Update Ubuntu
# apt update # apt upgrade
Step2: Install Python PIP And Prerequests
Installing Python and PIP
# apt install python3 python-is-python3 python3-dev pip
Installing Requirement Packages
# apt install net-tools git wget build-essential python3-wheel python3-suds python3-all-dev python3-venv \ python3-setuptools python3-tk libxml2-dev node-less libzip-dev libpq-dev libxslt1-dev libevent-dev \ libsasl2-dev libldap2-dev pkg-config libtiff5-dev libjpeg8-dev libjpeg-dev \ zlib1g-dev libfreetype6-dev liblcms2-dev liblcms2-utils libwebp-dev tcl8.6-dev \ tk8.6-dev libyaml-dev fontconfig xfonts-75dpi xfonts-base xfonts-encodings xfonts-utils libopenjp2-7-dev libharfbuzz-dev libfribidi-dev libxcb1-dev
Installing wk-html-to-pdf Tool
Wkhtmltopdf tool is a command-line utility to convert HTML to PDF or image using WebKit
# apt install wkhtmltopdf
Step3: Install And Configure PostgreSQL Database
Install and Enable Database
# apt install postgresql # systemctl enable postgresql
Create The Database User
We need to create the database user odoo , so we will use the sudo command to create a database user and password but run the command as the postgres
# sudo -u postgres createuser odoo -U postgres -dP
Step4: Add Odoo System User
Adding the new system user odoo and set its password, as the following
# adduser --system --home=/opt/odoo --group odoo
Step5: Install Odoo 15
Cloning Odoo 15 from Github
# git clone https://www.github.com/odoo/odoo --depth 1 --branch 15.0 /opt/odoo
Go to the odoo system user home directory, and create our odoovenv virtual environment, as it’s highly recommended to isolate Odoo to avoid any conflicts that may occur.
# cd /opt/odoo # python -m venv odoovenv
Active odoovenv Odoo Virtualenv and install Python wheel
# source odoovenv/bin/activate # pip install wheel
Install Odoo dependencies and requirements
# pip install -r requirements.txt
Deactivate the odoovenv
# deactivate
Create a custom Odoo addons directory
# mkdir odoo-extras-addons
Create an Odoo configuration template file with the following options, and set the database user and password we created in Step3 as the following
# vim /etc/odoo.conf [options] admin_passwd = set_odoo_admin_gui_password db_host = False db_port = False db_user = odoo db_password = odoo_db_password addons_path = /opt/odoo/addons,/opt/odoo/odoo-extras-addons
Create Odoo Systemd Unit
# vim /etc/systemd/system/odoo.service [Unit] Description=Odoo 15 Server Requires=postgresql.service After=network.target postgresql.service [Service] Type=simple SyslogIdentifier=odoo-server PermissionsStartOnly=true User=odoo Group=odoo ExecStart=/opt/odoo/odoovenv/bin/python3 /opt/odoo/odoo-bin -c /etc/odoo.conf StandardOutput=journal+console [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Adjustment files permissions
We need to change the ownership and files permissions of the odoo home directory
# chown -R odoo.odoo /opt/odoo # chmod -R 2755 /opt/odoo
If you are not a root while creating the systemd unit file, you will need to change the odoo.service file owner and permission.
Remember: You need to use sudo if you are not currently the root.
# chown root: /etc/systemd/system/odoo.service # chmod 755 /etc/systemd/system/odoo.service
Start The Odoo server and check the status
# systemctl daemon-reload # systemctl enable --now odoo # systemctl status odoo
# netstat -puntl Active Internet connections (only servers) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:8069 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 59377/python3 tcp 0 0 127.0.0.53:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 499/systemd-resolve tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 685/sshd: /usr/sbin tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:5432 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 56638/postgres tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:6010 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 791/sshd: root@pts/ tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 685/sshd: /usr/sbin tcp6 0 0 ::1:5432 :::* LISTEN 56638/postgres
You can see the Odoo server running and listening to port 8069, and PostgreSQL running and listening to port 5432 at localhost.
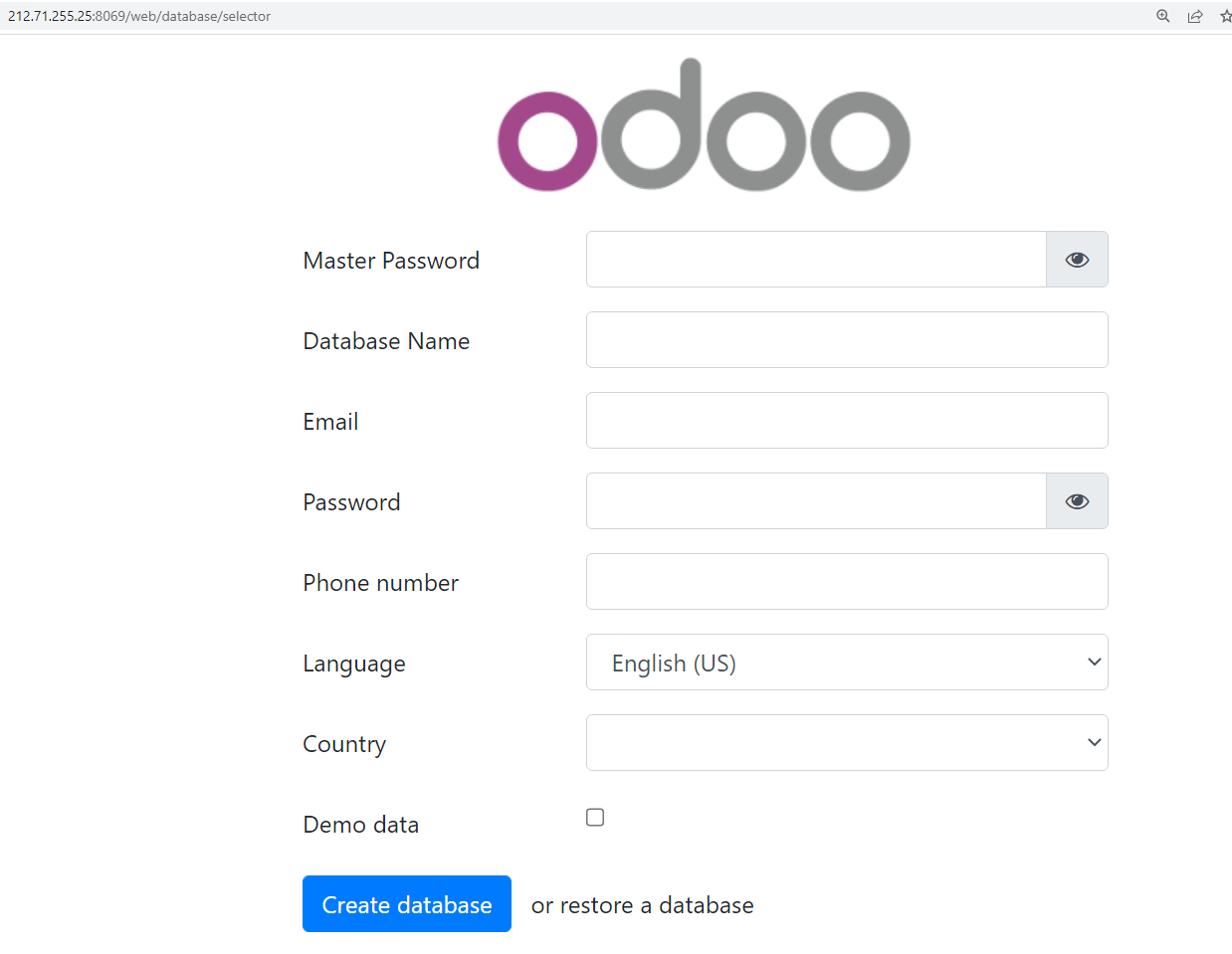
Now you can browse and access your Odoo using http://[Server_IP_Address]:8069, and continue the setup process by filling up the required information, and clicking the Demo data box if you want to test the system
Step6: Install And Configure Nginx As A Reverse Proxy
Install And Enable Nginx
# apt install nginx # systemctl enable nginx
Configure Nginx As A Reverse Proxy
Create the file odoo.conf at the path vim /etc/nginx/sites-available/odoo.conf, then append the following configuration into it.
PS: Do not forget to replace the domain name, and the IP-Address below with your server public IP-Address
# vim /etc/nginx/sites-available/odoo.conf
# Define Your Server To Listen To Your Plubic IP ADDRESS && HTTP Port 80
# Do not forget to replace Server Public IP-Address and domain name with yours.
# If you want to redirect www to non-www domain, uncomment the next server block.
#server {
# listen 212.71.255.25:80;
# server_name www.odoo-lab.com;
# access_log off;
# return 301 http://odoo-lab.com$request_uri;
#}
server {
listen 212.71.255.25:80;
server_name odoo-lab.com;
# We capture the logs
access_log /var/log/nginx/odoo-lab.com.log;
# Adjustment Headers
# Uncomment the next header if you are using Validation Certification To Force using it and setting up ssl cache age.
#add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=63072000; includeSubDomains; preload";
add_header X-Frame-Options SAMEORIGIN;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options nosniff;
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin *;
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Credentials true;
#Enable and configure GZIP
gzip on;
gzip_static on;
gzip_comp_level 9;
gzip_min_length 256;
gzip_proxied any;
gzip_vary on;
gzip_buffers 16 8k;
gzip_http_version 1.1;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
gzip_types
application/atom+xml
application/javascript
application/x-javascript
application/json
application/ld+json
application/manifest+json
application/rss+xml
application/vnd.geo+json
application/vnd.ms-fontobject
application/x-font-ttf
application/ttf
application/x-ttf
application/font-woff
application/x-font-opentype
application/x-web-app-manifest+json
application/xhtml+xml
application/xml
font/opentype
font/ttf
font/x-woff
image/bmp
image/svg+xml
image/x-icon
text/cache-manifest
text/css
text/javascript
text/plain
text/vcard
text/vnd.rim.location.xloc
text/vtt
text/x-component
text/x-cross-domain-policy;
# text/html is always compressed by gzip module
# To allow POST on static pages
error_page 405 =200 $uri$is_args$args;
location / {
# Pass Every request to Odoo at the Port 8069
proxy_pass http://212.71.255.25:869;
# Adjustement reverse proxy headers.
proxy_read_timeout 640;
proxy_connect_timeout 640;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto http;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Port 80;
proxy_buffers 16 32k;
proxy_buffer_size 64k;
proxy_request_buffering off;
proxy_buffering off;
}
# Enable Caching Static files...
location ~* \.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif|ico|css|js|pdf|ttf|woff|eot|bz2|gz|woff2|svg|bmp)$ {
proxy_pass http://212.71.255.25:8069;
proxy_read_timeout 640;
proxy_connect_timeout 640;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto http;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Port 80;
proxy_buffers 32 64k;
proxy_buffer_size 128k;
proxy_request_buffering off;
proxy_buffering off;
access_log off;
log_not_found on;
# Extend Browsers Caching Time for static file
expires 60d;
}
}
Create a symbolic link for the nginx odoo.conf file into the site-enabled directory as the following
# cd /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/ # ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/odoo.conf ./
Check the Nginx configuration file, then restart if OK.
# nginx -t nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful # systemctl restart nginx
You can access your Odoo using http://odoo-lab.com or your server public IP-Address.
To enable SSL access to your Odoo server, you will need to modify the Nginx config file as the one here: https://github.com/linuxlabz/wordpress-debian/blob/main/yourdomain_https.conf its enable SSL, and the file is similar lab and example we created in this article.
And you can create your self signed SSL in simple steps as described here: How to generate your self-signed SSL certificate in 3 Steps for Linux, Or you can create your validate SSL Certificate using Let’s Encrypt



